Customer Support
How to disable open DNS resolvers in a VPS
An Open DNS Resolver is a DNS server that responds to DNS queries from any IP address on the internet. This poses a serious security risk, as it can be exploited for DNS amplification DDoS attacks.
If your VPS operates as an open resolver, you may notice increased resource usage or receive an abuse report.
You can use the following recommended analysis tool to check this specific service and its behavior: https://dnsviz.net/
When is a VPS considered an Open DNS Resolver?
Your VPS is considered an open DNS resolver when:
- It responds to recursive DNS queries from external IP addresses
- There are no restrictions on who can use the DNS server
Linux Server – Checking and Disabling an Open DNS Resolver
Step 1: Check if the DNS server responds publicly
You can check whether your DNS server responds to queries from external IP addresses using the following command:
dig @YOUR_SERVER_IP google.comIf you receive a response, then the DNS resolver is publicly accessible.
Step 2: Check if a DNS service is running
Check whether a DNS service such as BIND is running:
systemctl status namedIf you are not using a DNS server on your VPS, it is recommended to disable it completely.
Step 3: Restrict DNS recursion in BIND
Open the BIND configuration file:
nano /etc/named.confor:
nano /etc/bind/named.conf.optionsIn the options section, ensure the following settings are present:
recursion no;
allow-query { localhost; };Save the file and restart the service:
systemctl restart namedStep 4: Restrict access via firewall
Even with proper DNS configuration, you must restrict access to port 53.
Example using iptables:
iptables -A INPUT -p udp --dport 53 ! -s 127.0.0.1 -j DROP
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 53 ! -s 127.0.0.1 -j DROPExample using firewalld:
firewall-cmd --remove-service=dns --permanent
firewall-cmd --reloadWindows Server – Disabling an Open DNS Resolver
Step 1: Check the DNS Server Role
- Connect to the VPS via Remote Desktop
- Open Server Manager
- Check whether the DNS Server role is installed
If you are not using DNS:
- Completely remove the role
Step 2: Disable DNS Recursion
- Open DNS Manager
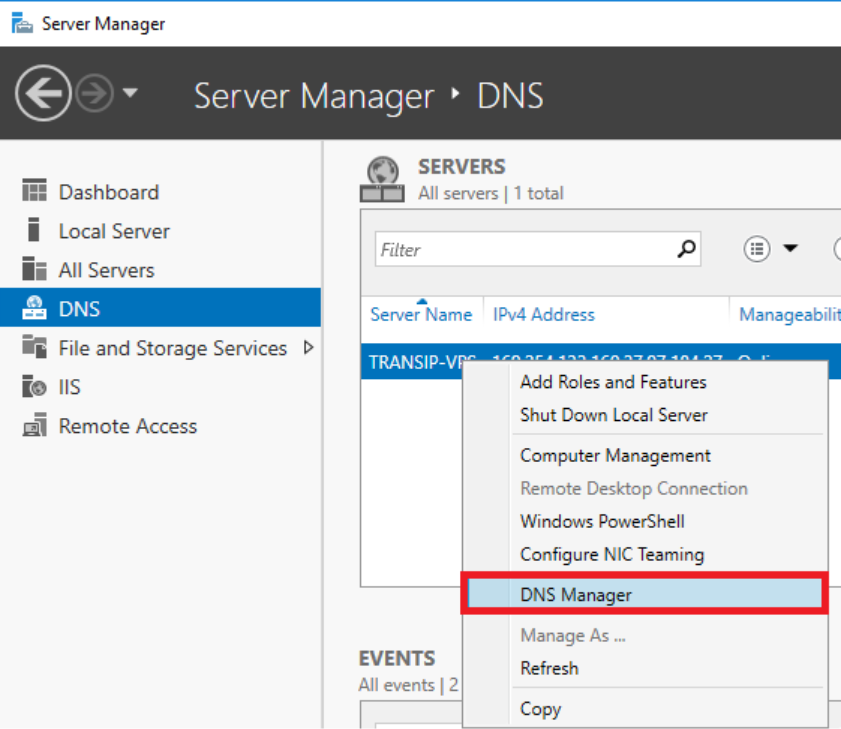
- Right-click on the server name
- Select Properties
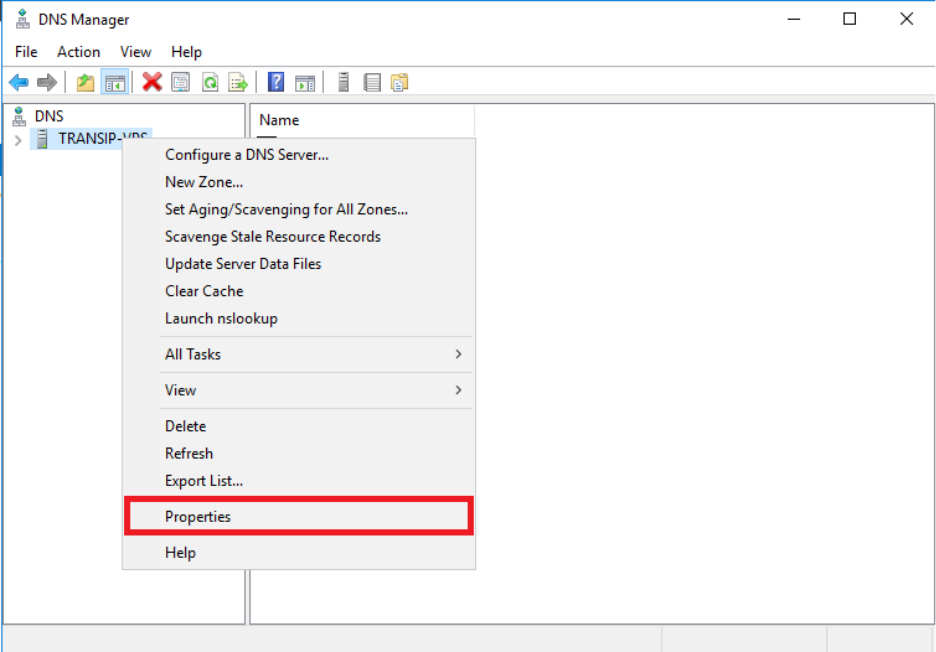
- Go to the Advanced tab
- Disable the Enable recursion option
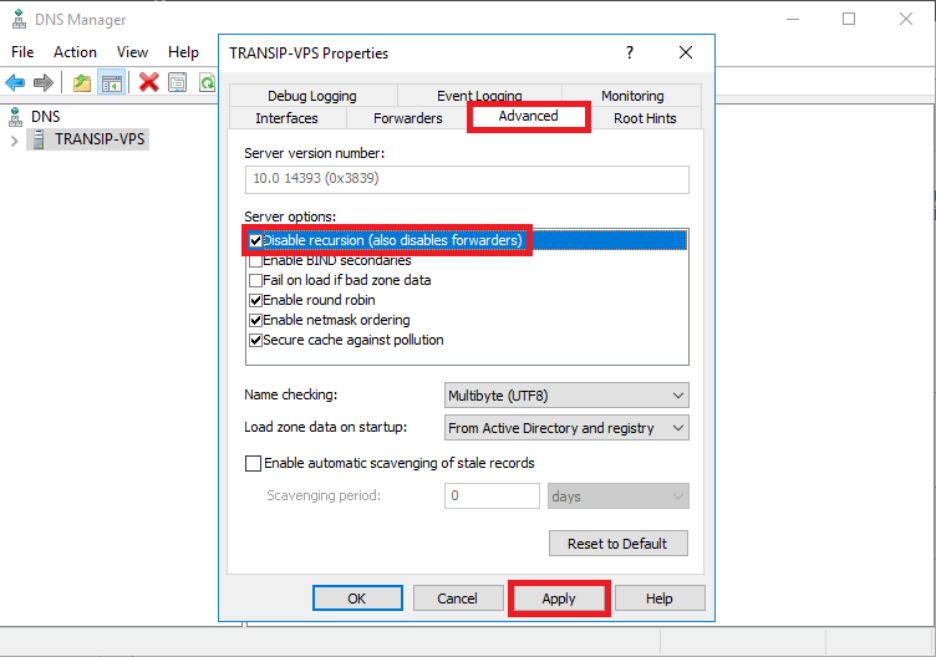
This prevents the server from responding to recursive DNS queries.
Step 3: Restrict access via Firewall
- Open Windows Defender Firewall
- Go to Inbound Rules
- Locate rules for DNS (TCP/UDP 53)
- Modify them so that:
- Access is allowed only from localhost or internal IP addresses
- All external IP addresses are blocked
If you do not require DNS:
- Completely disable the rules for port 53
What to do if you are not using DNS on your VPS
If your VPS does not function as a DNS server:
- Stop and disable the DNS service
- Close port 53 in the firewall
- Remove the DNS role (on Windows)
This is the safest configuration.
Conclusion
- Open DNS resolvers pose a serious security risk
- On Linux, you must:
- Restrict recursion
- Apply firewall rules
- On Windows, you must:
- Disable recursion
- Apply firewall restrictions
- If DNS is not required, complete deactivation is the recommended practice
You haven't found what you are looking for?
Contact our experts, they will be happy to help!
Contact us